datacasting
The AHC has been following the development of a "Datacasting" solution for the past year. This initiative is beginning to build interest and use cases in both the public (state and local) and in the private sector. Through the AHC's Multi-State Fleet Response Working Group's efforts of working with the key “lifeline” private sectors including electric, food, fuel, and rail, we have determined how to utilize this unique technology to enhance information sharing capabilities between the private sector and public sector. Some of this coordination is shown in our national Multi-State Fleet Working Group activities where the electric sector is helping us drive some of these information sharing requirements. Please feel free to review at www.fleetresponse.org/.
what is datacasting?
Since going all digital in 2000, broadcast
television transmits a stream of digital packets. They populate most of them with TV
programming aimed at consumers, but technology exists to allow a portion to be
used for encrypted computer data. When
using this capability called datacasting, public safety users get all the
benefit of the existing broadcast infrastructure operating on licensed spectrum
providing metropolitan wide coverage with resilient and redundant systems
monitored by full-time engineers.
An example is WHUT in Washington, DC is transmitting 3 million bits per second that the U.S. Park Police have used to send encrypted video and other secure data to their officers and others during large crowd events (watch HERE). Other data centric networks like cellular can become congested or even fail during emergencies, but broadcast television is never congested and is designed to withstand most severe weather events.
Datacasting is a computer-to-computer service utilizing small inexpensive ($300-$600) receivers which appear as a new wireless network path to an MDT in the field. The content is aimed at individuals or groups of people like talkgroups, only those targeted can see what is authorized for them to see – the public sees nothing. Groups can be separately targeted for concurrent use with divergent content, or targeting can span groups to improve interoperability as needed. It has been used for school security in Las Vegas (Clark County, fifth largest in the U.S.) for eight years (watch HERE).
An example is WHUT in Washington, DC is transmitting 3 million bits per second that the U.S. Park Police have used to send encrypted video and other secure data to their officers and others during large crowd events (watch HERE). Other data centric networks like cellular can become congested or even fail during emergencies, but broadcast television is never congested and is designed to withstand most severe weather events.
Datacasting is a computer-to-computer service utilizing small inexpensive ($300-$600) receivers which appear as a new wireless network path to an MDT in the field. The content is aimed at individuals or groups of people like talkgroups, only those targeted can see what is authorized for them to see – the public sees nothing. Groups can be separately targeted for concurrent use with divergent content, or targeting can span groups to improve interoperability as needed. It has been used for school security in Las Vegas (Clark County, fifth largest in the U.S.) for eight years (watch HERE).
how datacasting works
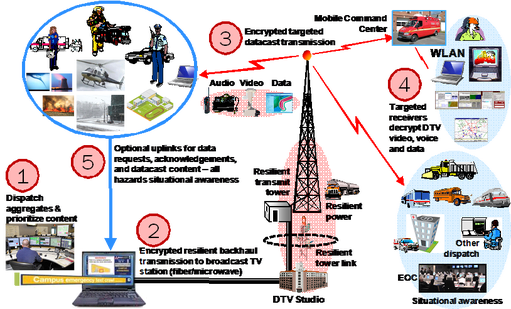
(1) Dispatch selects video, voice or data (e.g., floor plans, maps, photos, POC lists, helicopter video, etc.).
(2) Selected data is pushed to the TV station over a secure network.
(3) TV station immediately sends to transmitter for delivery to targeted receivers in the field.
(4) Recipients with proper receiver only get the data if they are on the target list.
(5) Existing data paths can be employed to provide a return path for local video and data, requests for new content and receipt acknowledgement.
Further use cases and description of datacasting
|
National Distribution Whitepaper
Secure Targetable Digital Television Datacast |
Keeping Up With the Crowds - HStoday.us
Datacasting- Utilization in Washington DC Fourth of July Event |
|
PBS to the Rescue - Securitymanagement.com
Datacasting- Utilized in Las Vegas School System |
Digital Television (DTV) Datacast for First Responders
Explanation, Precedence and Approach |
Frequently Asked Questions
1) Does Datacasting compete with or replace the FirstNet initiative?
No. Datacasting (e.g. digital television) has proven to be an effective use of existing resilient broadband infrastructure that can off-load wide-area broadcast communications from traditional LTE networks (e.g. FirstNet) particularly for bandwidth-intensive applications like live video content.
No. Datacasting (e.g. digital television) has proven to be an effective use of existing resilient broadband infrastructure that can off-load wide-area broadcast communications from traditional LTE networks (e.g. FirstNet) particularly for bandwidth-intensive applications like live video content.
2) Is Datacasting a 1-way or 2-way form of communications?
Today, Datacasting is a 1-way, broadcast only capability. This is changing. Over the next 2 years, this will evolve into a 2-way communications platform.
Today, Datacasting is a 1-way, broadcast only capability. This is changing. Over the next 2 years, this will evolve into a 2-way communications platform.